Multiple Hormonal Deficiencies in Anabolic Hormones in Frail Older Women
- Published in Hormones & Health

Reduced levels of anabolic hormones can contribute to aging and frailty. Most studies that have investigated this focused on the relationship between individual hormones and specific age-associated diseases. An interesting study in older women aged 70-79 years sought to examine the associations of individual anabolic hormonal deficiencies of free testosterone, IGF-1 and DHEA, and to assess their combined effects as well.[1]
Relationship between Low Levels of Anabolic Hormones and Mortality in Older Men
- Published in Hormones & Health

The anabolic hormones testosterone, IGF-1 and DHEA (a pre-hormone) are receiving more and more attention by health professionals because the anabolic-catabolic imbalance that favors catabolism is a key factor in accelerated physical deterioration aging.[1, 2] Anabolic impairment can speed up the age-related decline in muscle mass and physical performance, increase in fat mass, development of insulin resistance, cardiovascular risk factors, metabolic syndrome and diabetes, conditions that in turn affect mortality.[3-18]
Interestingly, low levels of multiple anabolic hormones, rather than a single one, has a stronger association with age related muscle loss and the frailty syndrome. [19, 20] In men with chronic heart failure, deficiency of more than one anabolic hormone identifies patients with higher mortality rates.[21]
An interesting study sought to investigate the relationship between parallel deficiency of several anabolic hormones and mortality in a general population of older men, regardless of coexisting disease:[22]
DHEA supplementation in older adults helps reverse arterial aging
- Published in DHEA

When it comes to health promotion and longevity, DHEA is a supplement which deserves more attention than it has been getting.
DHEA levels (the main circulating form of DHEA in the bloodstream is DHEAS) decrease approximately 80% between ages 25 and 75 year.[1, 2]This large decline in DHEA has led to interest in the possibility that aging related DHEA deficiency may play a role in the deterioration in physiological and metabolic functions with aging, and in the development of chronic diseases.
In support of this, it has been reported that DHEA level is negatively correlated with mortality and risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) (i.e. lower DHEA(S) levels are associated with higher mortality and CVD risk).[3-5]More recently it has been found that a steep decline or extreme variability over time in DHEA(S) levels is associated with higher mortality, more so than baseline DHEA(S) levels.[6]
Aging not only reduces DHEA(S) levels, but also results in an increase in arterial stiffness [7, 8], which is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk and mortality.[9-11]
It has been reported that DHEA levels are inversely associated with arterial stiffness (i.e. lower DHEA levels are associated with increased arterial stiffness. [7, 12, 13] Therefore, it is possible that DHEA replacement in older adults could reduce arterial stiffness, and thereby contribute to reduction in CVD and mortality...
DHEA - does it have any beneficial effects beyond testosterone and estrogen action?
- Published in DHEA
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) is most known for being a pro-hormone which in the body gets converted to testosterone and estrogen. It is a long held view that DHEA exerts all its effects via conversion to testosterone and estrogen. However, recent studies show that DHEA also has several health promoting non-hormonal actions...
DHEA 101
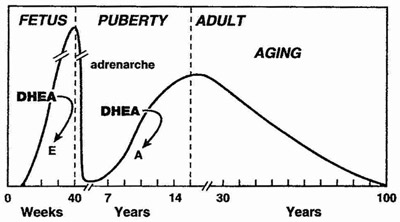
DHEA is produced mainly by the adrenal cortex, and is rapidly sulfated by sulfotransferases into DHEA-S. DHEA and its sulfated form DHEA-S is the most abundant steroid (pro)hormone circulating in the blood stream.[1] The sulfated from of DHEA has a longer half-life in the blood and its levels remain stable throughout the day, are not altered significantly by the menstrual cycle. When getting a blood test for DHEA, the fraction that is routinely measured is therefore DHEA-S. In response to metabolic demand, DHEA-S is rapidly converted back to DHEA (e.g. is hydrolyzed to DHEA by sulfatases).
DHEA levels decrease approximately 80% between ages 25 and 75 year.[2, 3] This large decline in DHEA spurred research interest in the possibility that aging related DHEA deficiency may play a role in the deterioration of physiological and metabolic functions with aging, and in the development of chronic diseases.



